Weather Forecast
Weather Forecast provides a 7-day forecast to anticipate the effects of the weather. The weather forecast is based on the longitude and latitude of the greenhouse and is therefore specific. The weather forecast is updated every hour, in order to steer greenhouse climate pro-actively. For example, when only little radiation is expected, watering can be stopped earlier in the afternoon. Or when a lot of radiation is expected during the day, the buffer tank is available for maximum CO2 production.
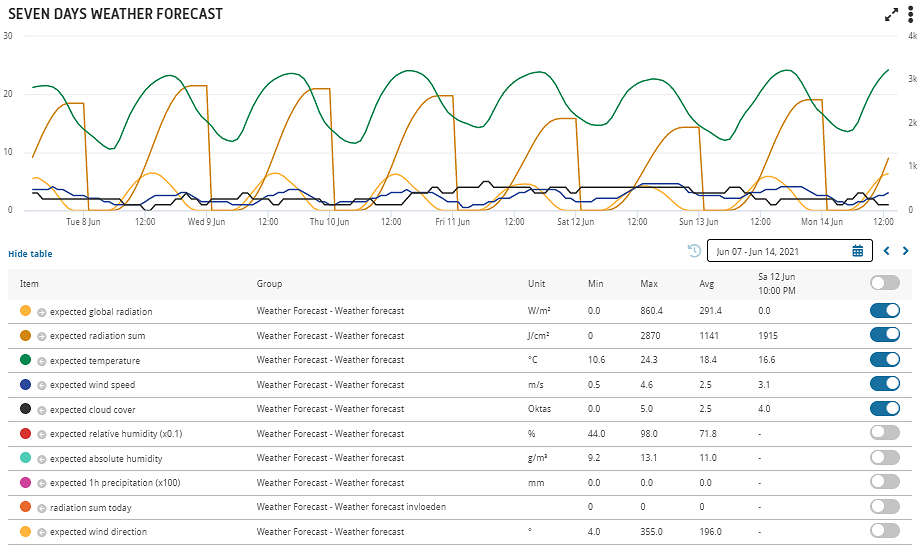
IIVO displays radiation forecasts for four periods of time. During the current clock hour (1) and current day (2) and for an adjustable number of hours according to time window A (3) and B (4).The image above shows the weather forecast for the next 7 days. It can be clearly observed that when the radiation intensity (expected global radiation) increases, the radiation sum also increases. Moreover when the radiation intensity decreases, the relative increase declines again.
Always be in control
The height of the radiation sum can be used as influence for example for screens, watering, heat storage and 24 hour temperature. We briefly explain the example at 24-hour temperature. It is known that the photosynthetic activity increases as radiation increases. Whenever, the radiation sum is high, the average 24-hour temperature can also increase proportionally to improve the photosynthetic efficiency. Similarly, IIVO can adjust the average 24-hour temperature to the expected radiation sum for that 24-hour period. Completely automatically. On the occasion that, the actual measured radiation sum deviates from the original expectation, IIVO also automatically adjusts the average 24-hour temperature again. Herewith, IIVO is your guide to always be in control.
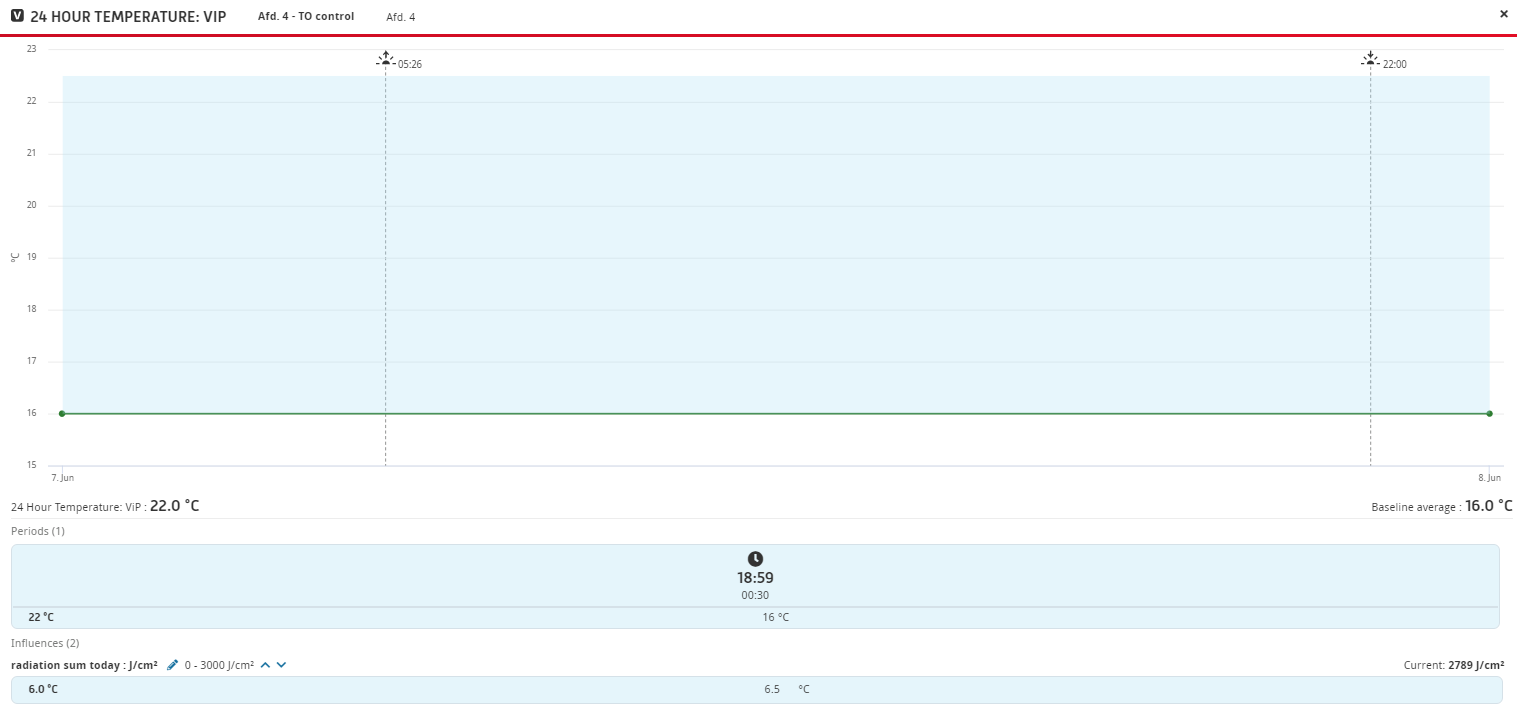
The image above shows an example of the 24-hour temperature adjustment by IIVO. In this example the expected radiation sum for the day is high. Therefore, the daily temperature should also increase based on plant physiological principles. At more than 3,000 J/cm2 the increase can be 6.5 °C. Based on the forecast of the day (2,367 J/cm2), an increase of 5.1 °C is desired to optimize growth.
Weather Forecast in practice
It turns out that the expected radiation according to Weather Forecast is used in practice in different ways. For instance in the following situations:
- Increasing the heating temperature; the higher the expected radiation sum, the higher the heating temperature during the day.
- Increasing the average daily temperature; the higher the expected radiation sum, the higher the average daily temperature.
- Increasing and decreasing the average 24-hour temperature; the lower the expected radiation sum, the lower the average 24-hour temperature and vice versa.
In all these examples it is also required to change the ventilation temperatures.. In examples 2 and 3, IIVO also adjusts the night temperature on the basis of Temperature Optimization Control (TO control) in order to achieve the set 24-hour temperature.
Radar Forecast
The rain forecast of IIVO is linked to an outdoor radar. The Radar Forecast software generates the current precipitation forecast half an hour in advance. The computer retrieves these images every 10 minutes, but if a rain shower approaches quickly, this is automatically adjusted to every 5 minutes. In this way by using the IIVO, growers always anticipate the most current situation. This ensures that crops remain dry in all (changing) weather conditions.
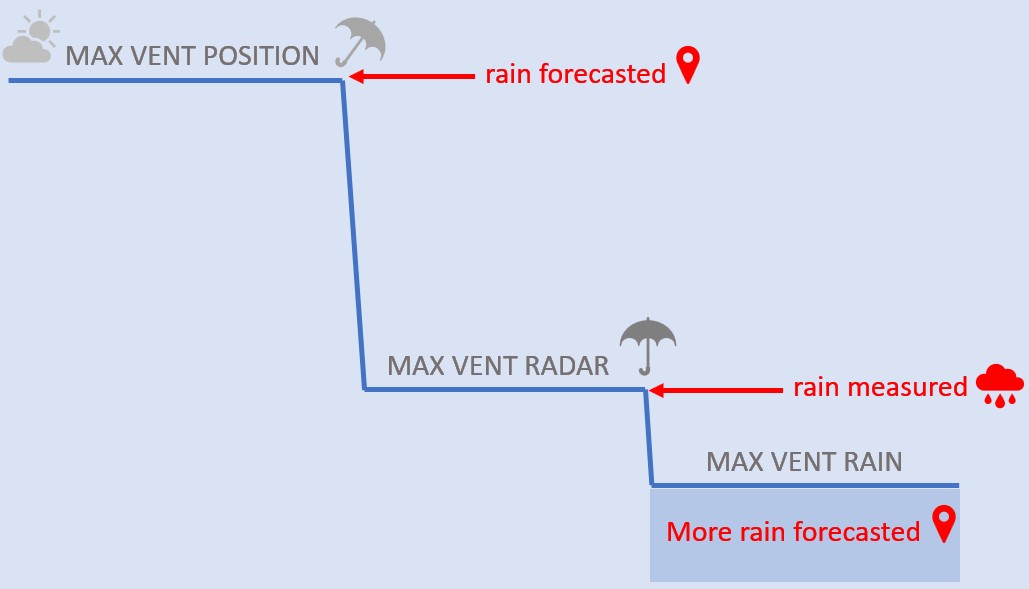
The figure below shows what happens once rain is expected. The maximum window position is reduced to (a new maximum) window position when rain is expected. As soon as it actually rains, the maximum window position is then reduced to the window position rain. The value of this is determined by the expected rain intensity.
Radar Forecast is currently available in North America. In the map below, the coverage can be seen.